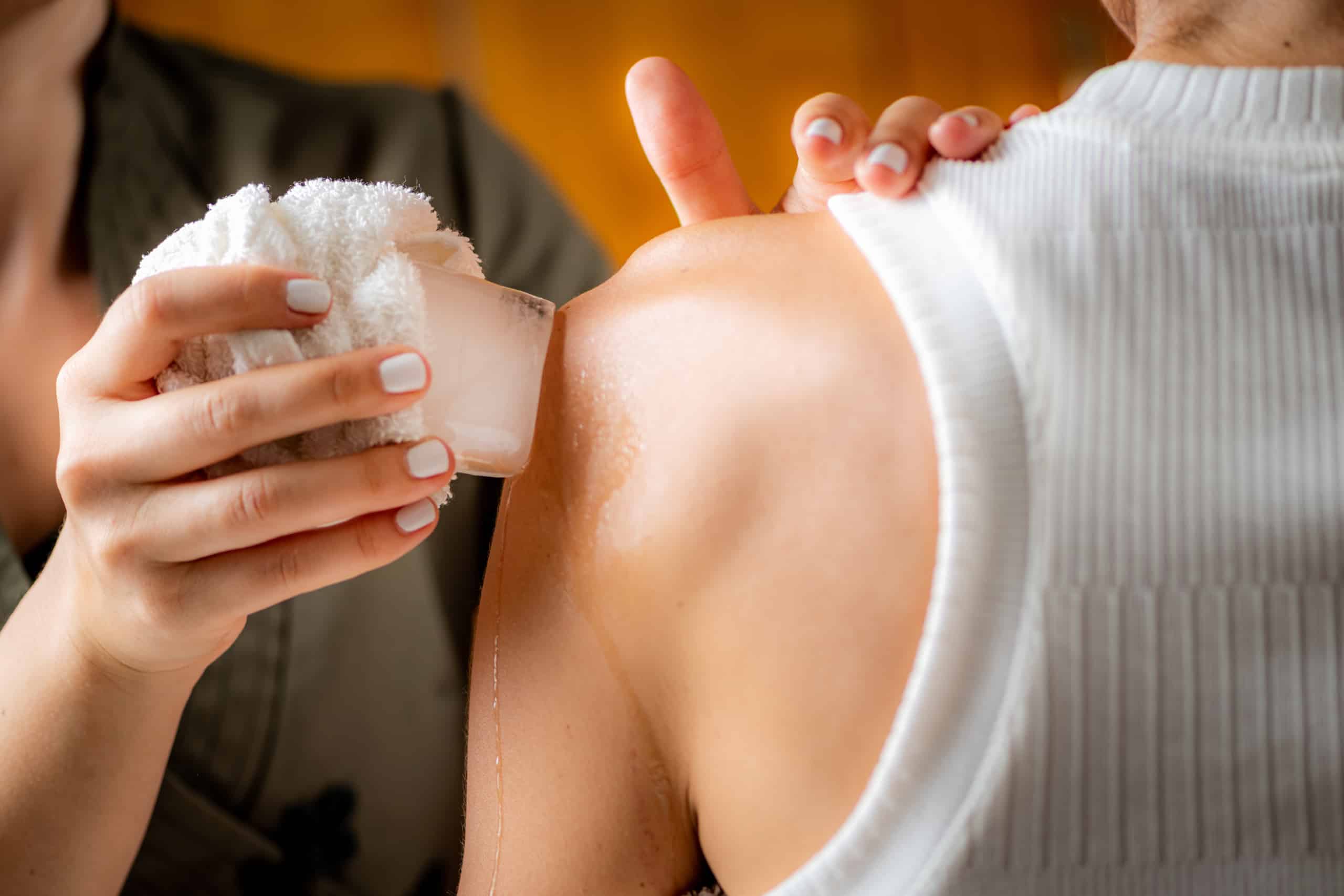
Introduction
Heat and cold therapy are two methods which reduce inflammation in the body. But what is the difference between them? This article will explain why each type is beneficial, and potential drawbacks to consider. We will also discuss techniques for utilizing heat and cold therapy safely.
Inflammation is when tissue is damaged, and molecules are released into cells. This response can lead to swelling, redness, pain, stiffness and fever.
- Heat treatments draw blood away from inflamed areas and increase circulation, which reduces swelling and relaxes muscles.
- Cold treatments reduce muscle spasms by causing vasoconstriction, which decreases blood flow and numbs surfaces to lessen pain.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is when the body reacts to an injury or infection. It causes chemicals from the immune system to arrive at the spot, leading to pain, swelling, redness and heat. Causes include injury, infections, autoimmune diseases and chronic conditions.
Heat and cold therapy are both types of treatments to fight inflammation.
- Heat therapy can be done with heating pads, hot baths or showers, and warm compresses. This increases blood flow; oxygen reaches injured tissue, flexibility develops in muscle tissue and muscle tension is reduced. Pain signals caused by inflammation are also lessened.
- Cold therapy involves ice packs or cold compresses on the painful area for 10-20 minutes. Swelling is reduced because cold temperatures make blood vessels constrict, and the numbing effect helps with minor aches and pains. Cold therapy should not be continued for too long, as this could lead to worse issues.
How Heat and Cold Therapy Can Help
Heat and cold therapy are two common treatments for reducing inflammation, swelling, and pain. Heat therapy helps increase circulation, reduce muscle spasms, and lessen joint pain. It can also help you relax. Cold therapy, however, is meant to reduce swelling, numb pain, and decrease inflammation.
In this article, we’ll talk about the advantages of heat and cold therapy and how it can help with inflammation:
- Heat therapy helps increase circulation, reduce muscle spasms, and lessen joint pain.
- Cold therapy is meant to reduce swelling, numb pain, and decrease inflammation.
Heat Therapy
Heat therapy is a go-to, non-invasive way to handle inflammatory and musculoskeletal issues. It’s an efficient and relatively cheap method to ease pain from conditions like arthritis, bursitis, tendonitis, muscle spasms, strains and sprains. Heat boosts circulation in the area and lowers signals of pain going to the brain.
When utilizing heat therapy, pick between hot and warm treatments. Warm treatments usually involve wet or moist heat sources like heating pads, hot baths or showers, hot towels and lotions with menthol or capsaicin ingredients. Hot treatments like paraffin wax baths or infrared lamps can reach deeper tissues but need to be used with care. These therapies can cause skin irritation or even burns if not utilized properly. Move the source of heat so that only one area is exposed at once and don’t keep it on for more than twenty minutes at a time before taking a break.
The most regular types of heat therapy to decrease inflammation are:
- Short wave diathermy (high frequency waves)
- Microwave diathermy (microwaves)
- Ultrasound (sound waves)
- Thermal wraps (moist packs)
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) units which use mild electric impulses to promote healing in soft tissues.
All these should be discussed with your health care provider to decide which is best for your condition before beginning any kind of treatment plan.
Cold Therapy
Cold therapy uses cold (such as ice packs or gel packs) to reduce inflammation and pain. It slows down tissue breakages and spastic muscles. It helps with post-exercise soreness, post-operative swelling and chronic conditions like fibromyalgia.
Care should be taken with cold therapy, as it can cause frostbite and nerve injuries. Limit use to 15-20 minutes, no more than 3 times a day. Methods include:
- Ice packs/gel packs
- Ice baths/immersion coolers
- Cryo/cold chambers
- Cryotherapy machines (like an ice compression wrap).
When correctly used, cold therapy reduces edema, eases pressure on nerves and relieves pain without the need for medicines. It can also improve stiffness and spasticity caused by neurological disorders. It reduces muscle spasm and increases mobility.
Benefits of Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can both aid in reducing inflammation and providing pain relief. Heating up helps with boosting circulation, easing muscle tension, and relaxing cramped muscles. Cold therapy, on the other hand, has the power to reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
Let’s explore the advantages of using heat and cold therapy to reduce inflammation:
Pain Relief
Heat and cold therapy are used to relieve pain. Heat helps by improving blood flow, which relaxes muscles and reduces joint stiffness. Cold reduces inflammation by calming spasms, pain and swelling. Both therapies aid in injury recovery and work better together.
Hotwater bottles, hot packs, and warm compresses increase circulation in muscle tissues. Cold packs constrict vessels, which stops chemicals causing swelling. Heat from microwavable pads or dry heating pads relieves aches, pains, tension headaches, and myofascial trigger points. Cold therapies like ice massage and cold wraps made with gel-packs reduce back pain by lowering tissue temperature.
When dealing with injuries, it’s important to know when to apply heat and cold. Swollen joints should get cold therapy first, as heat increases swelling. Chronic stiffness and muscle soreness need heat therapy. Ice is for sudden flare-ups between treatments, like after strenuous activity.
Reduced Swelling
Heat and cold are both forms of therapy that can help with swelling and inflammation in the body. Heat therapy is used to increase blood flow in the tissues. This reduces pain, stiffness and inflammation. Cold therapy decreases swelling and inflammation by slowing down blood flow to the affected area. This helps it to heal faster and with less discomfort.
Heat therapy is often used after injuries or surgery. It can be an alternative treatment for sprains, pulled muscles, tendinitis, bursitis and other soft tissue inflammations. Heating pads or wraps filled with warm water, or gel packs heated in microwaves or boiling water, are common heat therapies. Fifteen minutes of heat several times a day can provide relief from pain and stiffness.
Cold therapy should start soon after an injury. It reduces swelling by slowing down fluid that goes into injured tissues. Ice packs are usually used. These can be gel packs stored in a freezer, or frozen vegetables wrapped up in cloths. For small areas on hands and feet, a thin layer of cloth should go between skin and the ice pack to stop frostbite. Cold therapy typically lasts 5-10 minutes. Both heat and cold should not go over 20 minutes at once. Prolonged use can cause tissue damage, even if there is no discomfort. Other treatments like exercise or massage should be used with heat and cold for better results.
Improved Mobility
Heat can be used to treat musculoskeletal injuries. It increases blood flow and sends essential nutrients for pain relief and healing. Heat therapy also relaxes muscles and reduces stiffness. It also slows down nerve conduction velocity, which helps to reduce pain.
Cold therapy is best for acute injuries. It reduces inflammation by numbing nerve endings and decreases pain signals sent to the brain. Cold therapy also decreases swelling and tight joints, leading to improved function, strength, and range of motion. Finally, cold therapy reduces capillary dilation and stimulates vasoconstriction, which minimizes bleeding into tissues.
Potential Risks of Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapies can ease pain. They work on blood vessels and reduce inflammation. But, there are things to consider. Heat and cold can burn skin if left too long. People with diabetes or poor circulation should talk to their doctor first. Areas without sensation due to nerve damage or paralysis should not use these treatments.
Rapid temperature changes may cause muscle tensions, pulled muscles, and other tissue damage. Start with lower temperatures. Increase only if needed after watching your body’s response. Pay attention to burning, freezing, or increased pain. Never put an ice pack directly on skin. Put a damp cloth over an ice pack instead. If discomfort comes, reduce the temperature until it stops. Then, continue at more comfortable levels.
Conclusion
To wrap up, using heat and cold therapy both work to reduce inflammation and pain. Heat therapy can help ease muscle spasms, joint stiffness and improve blood flow. Cold therapy helps lessens swelling, reduces nerve pain, triggers endorphins for stronger pain relief and increases range of motion.
Before using either treatment, it’s important to think about any underlying health issues that may be sensitive or risky. If you’re still in pain or the treatments don’t help, it’s best to talk to a healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the role of heat therapy in reducing inflammation?
Heat therapy increases blood flow to the affected area, which helps to reduce inflammation by improving the body’s ability to remove harmful toxins and increasing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the inflamed tissues.
2. Can cold therapy also help reduce inflammation?
Yes, cold therapy can be very effective in reducing inflammation by slowing down the flow of blood to the affected area, which reduces swelling and pain. Cold therapy can also be helpful in numbing the area and providing temporary relief from pain.
3. When should I use heat therapy and when should I use cold therapy?
In general, heat therapy is best used for chronic conditions, such as arthritis, where there is no active inflammation present. Cold therapy is most effective for acute injuries, such as sprains or strains, where there is active inflammation present.
4. What are some common heat therapy techniques?
There are a variety of heat therapy techniques, including using a heating pad, warm towels, hot water bottles, and heating creams or gels. It’s important to never use heat therapy for more than 20 minutes at a time and to always use a barrier to protect the skin from burns.
5. What are some common cold therapy techniques?
Some common cold therapy techniques include ice packs, gel packs, frozen vegetables, and cold water baths. It’s important to never apply ice directly to the skin and to always use a barrier to protect the skin from frostbite.
6. Are there any risks associated with heat or cold therapy?
Both heat and cold therapy can have risks, including burns, frostbite, or skin damage. It’s important to always follow proper safety precautions, such as using a barrier between the skin and the heat or cold source, and never applying heat or cold therapy for longer than recommended.